We all know that according to different heat dissipation methods, chillers can be divided into air-cooled chillers and water-cooled chillers. What is the difference between air-cooled chillers and water-cooled chillers?
1. The air-cooled chiller uses copper tubes and aluminum fins to dissipate heat from the condenser. A fan is required to blow the outdoor air through the heat exchange fins and take away the heat of the condenser, so the air-cooled chiller does not need to be connected to the cooling tower. But compared with water-cooled chillers, under the same power, air-cooled chillers have larger equipment size and higher noise. The condenser of water-cooled chillers exchanges heat with the cooling water from the cooling tower through the heat exchanger. The excess waste heat will be transported to the cooling tower through the cooling water loop and released into the atmosphere, or enter the water-water heat exchanger or soil heat exchange coil for storage. Therefore, water-cooled chillers do not need fans to dissipate heat, but need cooling towers or water (ground) source heat exchange pipelines. Water-cooled chillers have one more cooling water system than air-cooled chillers. The size of the unit of the same power is smaller than that of the air-cooled chiller, it does not take up space, and the noise is lower, but it needs a cooling tower and the equipment needs a computer room.
2. In terms of refrigeration and heat exchange switching, the air-cooled chiller-type refrigerant loop switches the flow direction through a four-way valve to exchange the condenser and the evaporator. In summer, heat is transferred from indoor to outdoor, and in winter, it absorbs heat from outdoor. indoor. The water-cooled chiller does not have the ability of evaporator and condenser interchangeability, so the unit connected to the cooling tower does not have the heating function (requires an external boiler). The heat pump unit needs to switch the chilled water and cooling water loops, and 8 water circuit switching valves are added in the machine room. In summer, cold water enters the house, hot water enters the external coil, and winter hot water enters the house, and cold water enters the external coil. (Some small water source heat pump units also have refrigerant four-way valves)
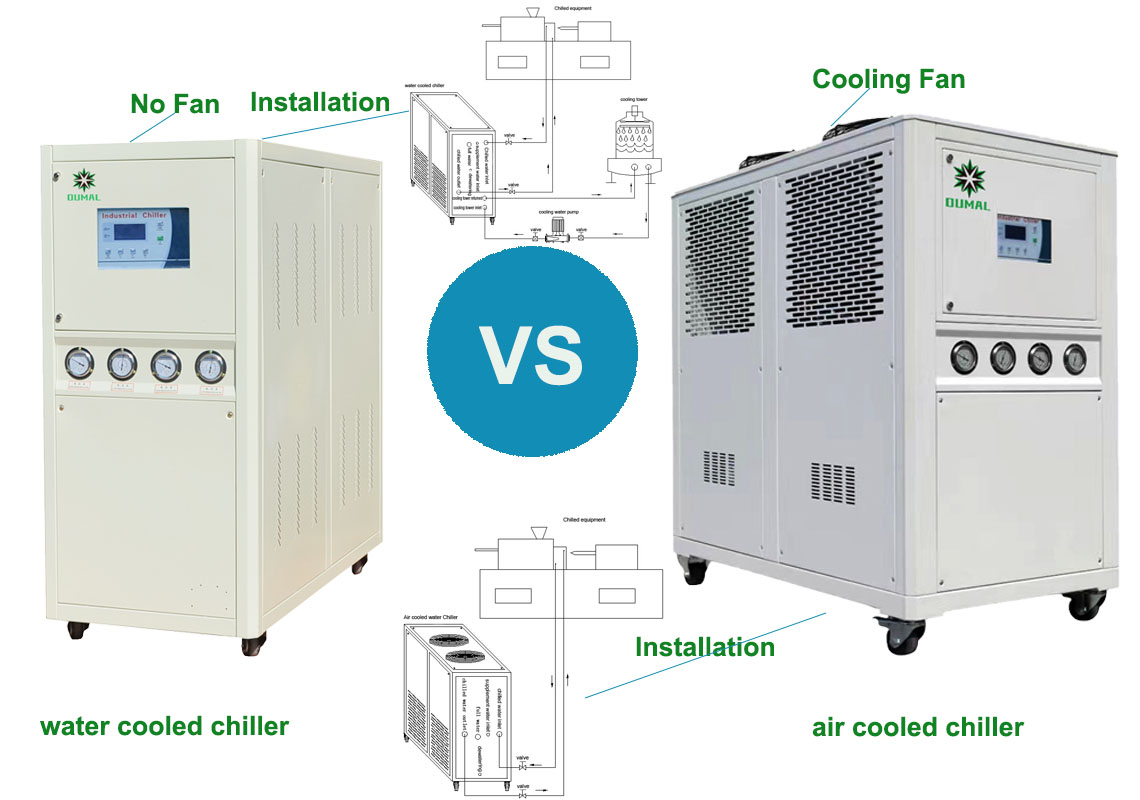
3. In the case of the same cooling capacity, the model of water-cooled chiller is smaller, because the energy efficiency ratio of water-cooled chiller is higher than that of air-cooled chiller, and the compressor of air-cooled chiller is better than water-cooled chiller. Great horsepower.
4. In terms of installation, the air-cooled chiller is easy to install, while the installation pipeline of the water-cooled chiller is more complicated.
If you don’t know whether to choose an air-cooled chiller or a water-cooled chiller when choosing a chiller, you can contact us. We will recommend to you a suitable chiller based on your on-site installation, the budget of the chiller, and the size of the model. Email: oumal@oumal.com
